Bitumen emulsions CSS
Bitumen emulsions CSS are usually made by passing the mixture of hot bitumen and water phase between a rotating disc, cone or wheel and a stator.
In the emulsification process, hot binder is mechanically separated into minute globules and dispersed in water treated with a small quantity of emulsifying agent.
The water is called the continuous phase and the globules of binder are called the discontinuous phase.
by proper selection of an emulsifying agent and other manufacturing controls, emulsified asphalts are produced in several types and grades
By choice of emulsifying agent, the emulsified asphalt may be:
(1) Anionic - binder globules are electro-negatively charged.
(2) Cationic - binder globules are electro-positively charged.
Also, by variation in materials and manufacture emulsified asphalts of both anionic and cationic types are made in several grades. Some of these grades and their uses are:
(1) Anionic - non -virginia grades RS-2 Tack and seal coat, SS-1h slow set slurry and tack,
(2) Cationic - virginia grades CSS-2 Tack and seal coat, CSS-1 tack, CSS-1h tack css-1h two types for slurry (rapid set and slow set) and tack; CSS-2 prime, tack, seal, and cold mix. (contains 7-12% solvent) because particles having a like electrostatic charge repel each other, asphalt globules are kept apart until the emulsion is deposited on the surface of the soil or aggregate particles. Emulsified asphalts can be used with cold as well as heated aggregates, and with aggregates that are dry, damp, or wet.
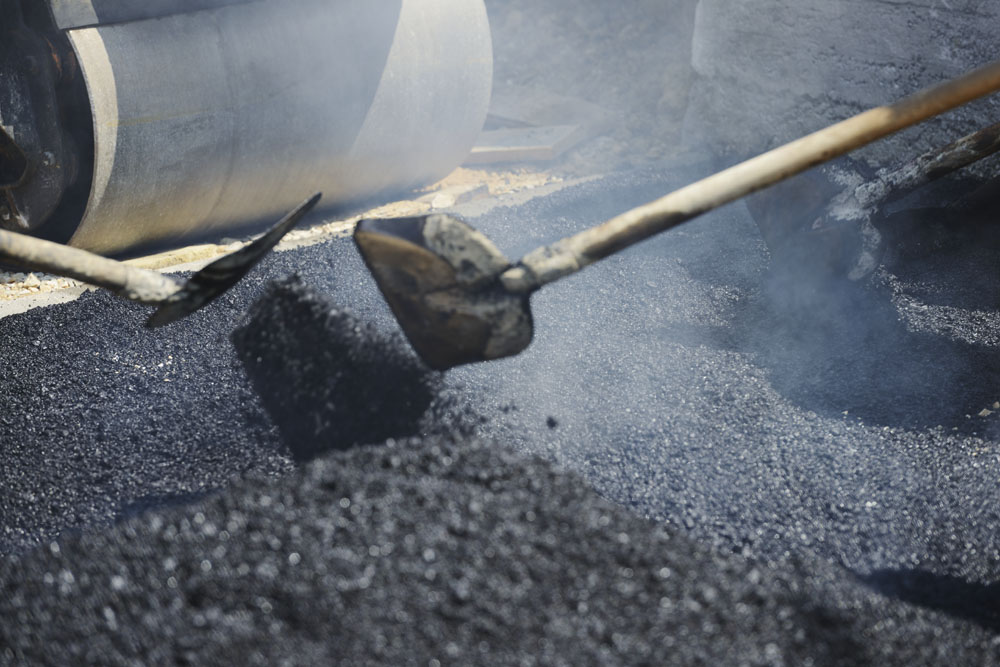
Application of emulsion bitumen CSS:
The advantages of asphalt emulsions CSS are related to their chemical and physical makeup, these advantages lead directly to the applications to the applications in which emulsions are used.
Sealing (CSS-1, CSS-2, m-80, vprime, precoating emulsion)
Slurry surfacing (cqs, cqs-1h, lmcqs, microsystems)
Patching/crack filling (css,css-r, CSS, CSS-r, ss-1)
Fog seal (ss-1, css, css-r, CSS, CSS-r)
Cold mix (CSS, CSS-r, specialty emulsions)
Tack coating (CSS-1, css, ss-1, specialty emulsions).
Dust laying (css,ss-1, specialty emulsions)
Stabilization/ recycling. (css, CSS, specialty emulsions).
Water proofing / roofing/ home. (specialty emulsions).
Agriculture. (ss-1, CSS, specialty emulsions).
Data Sheet of emulsion bitumen:
| PROPERTY | UNIT | SPEC. | METHOD |
| Kinematic Viscosity 50°C | Centistokes (CST) | 20-100 | ASTM D2170 |
| Residue on Sieving, 600 Micron IS | Mass Percentage (%) | 0.05 max | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability after 24 hours | Percentage (%) | 2 max | ASTM D244 |
| Binder Residue by Evaporation | Percentage (%) | 50 min | ASTM D244 |
| Setting Time | Minutes (′) | 15 | ASTM D244 |
| Penetration, 50 °C | 1/10 Millimeters (mm) | 60-200 | ASTM D5 |