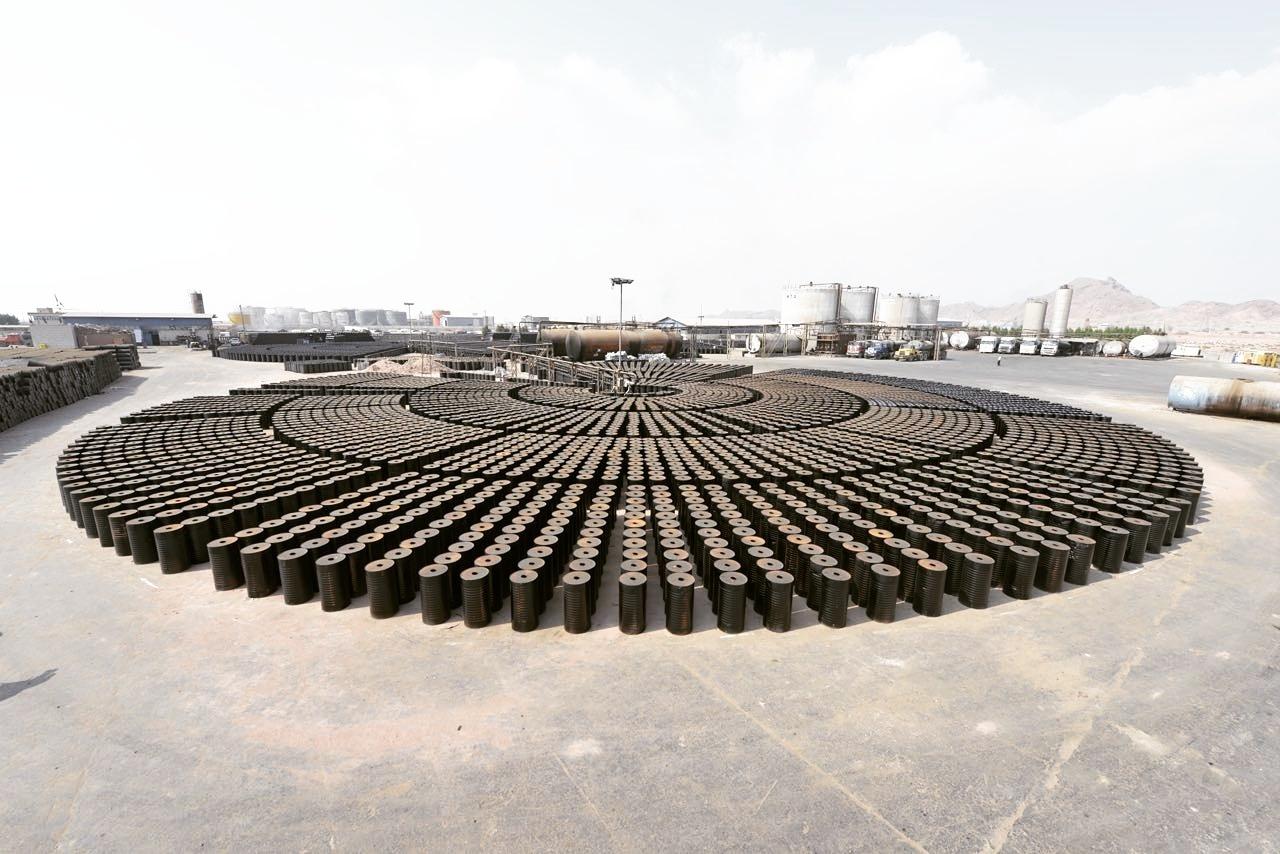
What is cutback bitumen?
Cutback bitumen is a range of binders that are produced by blending (mixing) penetration grade bitumen and a hydrocarbon solvent, such as paraffin or mineral turpentine.
When the solvent has evaporated, the binder returns to its original penetration grade to tie the particles together.
Cutback bitumen gets its name from the solvent that is involved in the process, because the solvent "cuts back" or evaporates, leaving behind the binder to "get on with the job".
The solvent used in cutback bitumen is called the "cutter" or "flux".
Three types of solvents are used for the blending process:
- slow curing (SC)
- medium curing (MC)
- rapid-curing (RC)
Advantage of cutback bitumen:
it can be applied at lower temperatures than penetration grades because of its lower Bitumen Solvents viscosity. A disadvantage is that cutback bitumen consumes non-renewable energy resources which are ultimately lost through evaporation.Applications of Cutback Bitumen:
Prime and Tack Coating The process of priming involves applying a low viscosity binder to a prepared but usually unbound aggregate base.
It is intended to be absorbed by the top layers of the base and provide a surface more easily ‘wetted’ by a subsequent bituminous covering.
The primer will be able to carry traffic for a short time (although this practice is uncommon) and help control dust.
Generally, primers are applied at rates between 0.5 and 1.4 L/m2.
Cutback bitumen's suitable for priming are also used for tack coats, which are applied to an underlying surface to help with the adhesion of subsequent asphalt layer.